Dancing#
Free will, freedom in fetters, dancing in chains#
From the point of view of form, the
archetypeof all the arts is the art of the musician.-Oscar Wilde 31
1. Phonetics
\
2. Temperament -> 4. Modes -> 5. NexToken -> 6. Emotion
/
3. Scales

Dancing in Chains. But these are old conversations about scholarship, politics, and art. The phrase “dancing with chains” (or “dancing in chains”) itself is over a century old: Friedrich Nietzsche used it in 1880 to describe constraining conventions that limit artistic innovation. 1 The Chinese poet Wen Yiduo used it in the 1930s to suggest that constraints provoke more imaginative art. The entire history of African American literature [and music!] since the enslaved poet Phillis Wheatley is a matter of negotiating real chains as well as metaphorical ones. This was the topic that brought me to China, in fact. 32. The idea of “conditional free will” came to me as a counterpoint to neuroendocrine determinism espoused by Sapolsky 33 34 or an idea from William James that the definition of “free will” is necessarily the definition of an illusion. I woke up this morning and declared that free will as an aesthetic experience, where the agent “dances in chains,” an interplay between freedom and constraint. It suggests that even within the upstream boundaries set by deterministic forces, downstream there’s room for creativity, expression, and agency—much like a dancer who finds elegance and grace within the limitations of choreography. Such constraint implies that true freedom lies not in the absence of constraints but in how skillfully one navigates within them. Just as an artist might create within the boundaries of a medium or genre or a dancer might express themselves within the limits of a routine, free will can be seen as the art of making choices within the confines of external and internal determinants. Viewed this way, an aesthetic autonomy emerges as a form of aesthetic expression. It’s about how we craft our lives, make decisions, and exert influence in the face of limitations. The constraints are not merely obstacles; they are part of what makes the exercise of free will meaningful and beautiful. There is elegance in such agency. Free will lies in the way one harmonizes with the constraints, finding freedom in the rhythm and flow of life’s given conditions. It’s about turning limitations into opportunities for creative and purposeful action, much like a dancer turns a restricted stage into a space for graceful movement - a freedom in fetters, a princely freedom. 35 There is philosophical depth as this view acknowledges that while absolute freedom might be an illusion, the manner in which we navigate relative to our constraints can be profound, purposeful, and even artistic. It transforms the discussion of free will from a binary question of “does it exist or not?” to a richer exploration of how we iteratively live, choose, and express ourselves within the framework we’re given. The beauty of life lies in how we exercise our agency within the bounds we face—an elegant dance within the chains of reality.#
\(\mu\) Fractals, God#
\(f(t)\) Phonetics:
Fractals\(440Hz \times 2^{\frac{N}{12}}\), \(S_0(t) \times e^{logHR}\), \(\frac{S N(d_1)}{K N(d_2)} \times e^{rT}\)
Show code cell source
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Parameters
sample_rate = 44100 # Hz
duration = 20.0 # seconds
A4_freq = 440.0 # Hz
# Time array
t = np.linspace(0, duration, int(sample_rate * duration), endpoint=False)
# Fundamental frequency (A4)
signal = np.sin(2 * np.pi * A4_freq * t)
# Adding overtones (harmonics)
harmonics = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] # First few harmonics
amplitudes = [0.5, 0.25, 0.15, 0.1, 0.05, 0.03, 0.01, 0.005] # Amplitudes for each harmonic
for i, harmonic in enumerate(harmonics):
signal += amplitudes[i] * np.sin(2 * np.pi * A4_freq * harmonic * t)
# Perform FFT (Fast Fourier Transform)
N = len(signal)
yf = np.fft.fft(signal)
xf = np.fft.fftfreq(N, 1 / sample_rate)
# Plot the frequency spectrum
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(xf[:N//2], 2.0/N * np.abs(yf[:N//2]), color='navy', lw=1.5)
# Aesthetics improvements
plt.title('Simulated Frequency Spectrum of A440 on a Grand Piano', fontsize=16, weight='bold')
plt.xlabel('Frequency (Hz)', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=14)
plt.xlim(0, 4186) # Limit to the highest frequency on a piano (C8)
plt.ylim(0, None)
# Shading the region for normal speaking range (approximately 85 Hz to 255 Hz)
plt.axvspan(500, 2000, color='lightpink', alpha=0.5)
# Annotate the shaded region
plt.annotate('Normal Speaking Range (500 Hz - 2000 Hz)',
xy=(2000, 0.7), xycoords='data',
xytext=(2500, 0.5), textcoords='data',
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', arrowstyle="->"),
fontsize=12, color='black')
# Remove top and right spines
plt.gca().spines['top'].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines['right'].set_visible(False)
# Customize ticks
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
# Light grid
plt.grid(color='grey', linestyle=':', linewidth=0.5)
# Show the plot
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Show code cell output
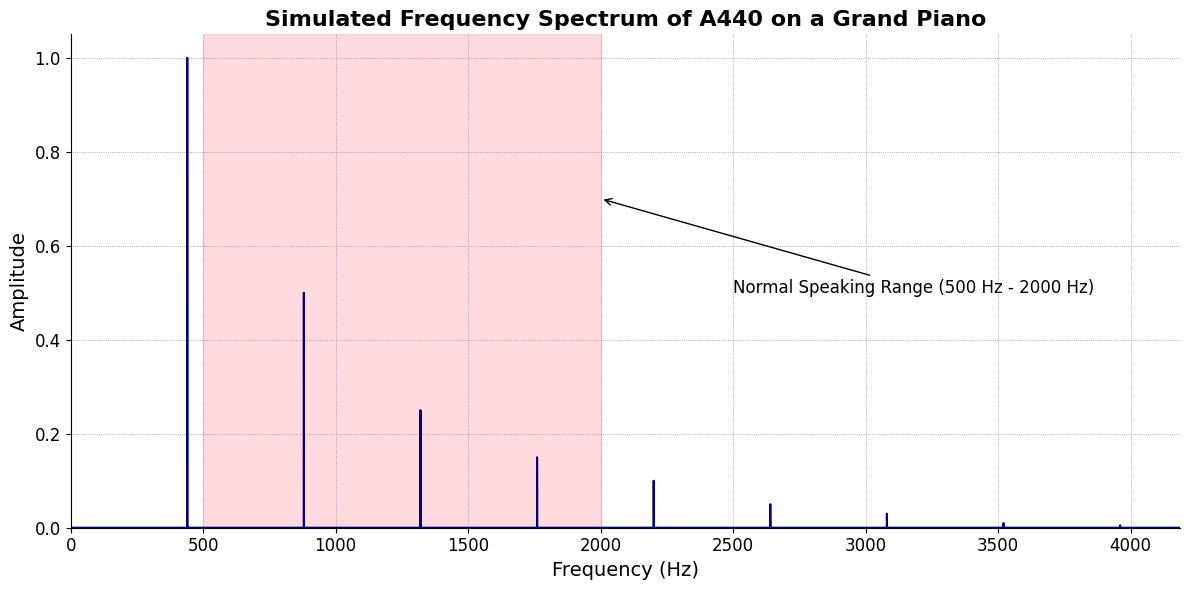
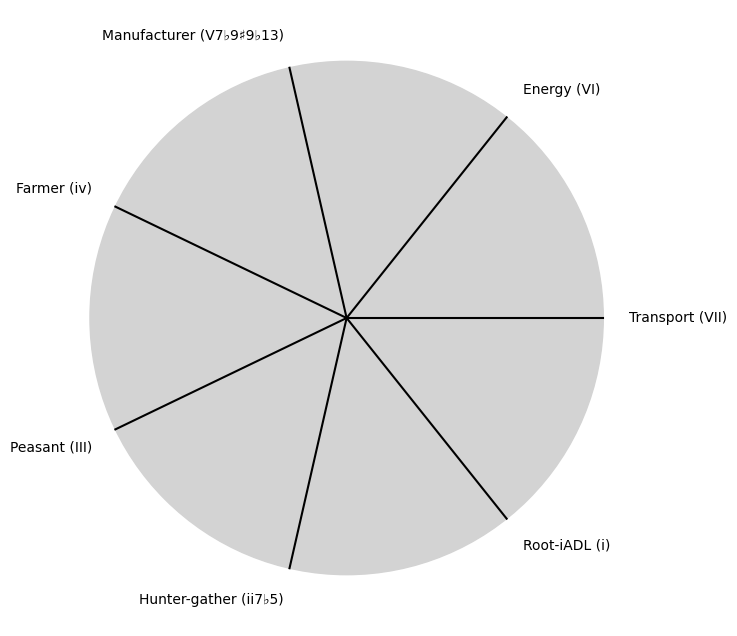
\(S(t)\) Temperament:
ChainsEqual temperament, Proportional hazards, Homoskedastic volatility\(h(t)\) Scale:
Equations1 Inherited, Added, Overcome
\(\sigma\) Chains, Neighbor#
\((X'X)^T \cdot X'Y\): Mode: \( \mathcal{F}(t) = \alpha \cdot \left( \prod_{i=1}^{n} \frac{\partial \psi_i(t)}{\partial t} \right) + \beta \cdot \int_{0}^{t} \left( \sum_{j=1}^{m} \frac{\partial \phi_j(\tau)}{\partial \tau} \right) d\tau\) .
Accidentsmezcal, mezclar, mezcaline. Just a reminder that accidents can mislead one to perceive patterns where there’s no underlying process responsible for them. That said, \(\alpha\) & \(beta\) are emerging as parameters representing the highest hierarchy in this multilevel dataset. They stand for determined (chains) & freewill (wiggle-room)
Show code cell source
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Clock settings; f(t) random disturbances making "paradise lost"
clock_face_radius = 1.0
number_of_ticks = 7
tick_labels = [
"Root-iADL (i)",
"Hunter-gather (ii7♭5)", "Peasant (III)", "Farmer (iv)", "Manufacturer (V7♭9♯9♭13)",
"Energy (VI)", "Transport (VII)"
]
# Calculate the angles for each tick (in radians)
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, number_of_ticks, endpoint=False)
# Inverting the order to make it counterclockwise
angles = angles[::-1]
# Create figure and axis
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
ax.set_xlim(-1.2, 1.2)
ax.set_ylim(-1.2, 1.2)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# Draw the clock face
clock_face = plt.Circle((0, 0), clock_face_radius, color='lightgrey', fill=True)
ax.add_patch(clock_face)
# Draw the ticks and labels
for angle, label in zip(angles, tick_labels):
x = clock_face_radius * np.cos(angle)
y = clock_face_radius * np.sin(angle)
# Draw the tick
ax.plot([0, x], [0, y], color='black')
# Positioning the labels slightly outside the clock face
label_x = 1.1 * clock_face_radius * np.cos(angle)
label_y = 1.1 * clock_face_radius * np.sin(angle)
# Adjusting label alignment based on its position
ha = 'center'
va = 'center'
if np.cos(angle) > 0:
ha = 'left'
elif np.cos(angle) < 0:
ha = 'right'
if np.sin(angle) > 0:
va = 'bottom'
elif np.sin(angle) < 0:
va = 'top'
ax.text(label_x, label_y, label, horizontalalignment=ha, verticalalignment=va, fontsize=10)
# Remove axes
ax.axis('off')
# Show the plot
plt.show()
Show code cell output
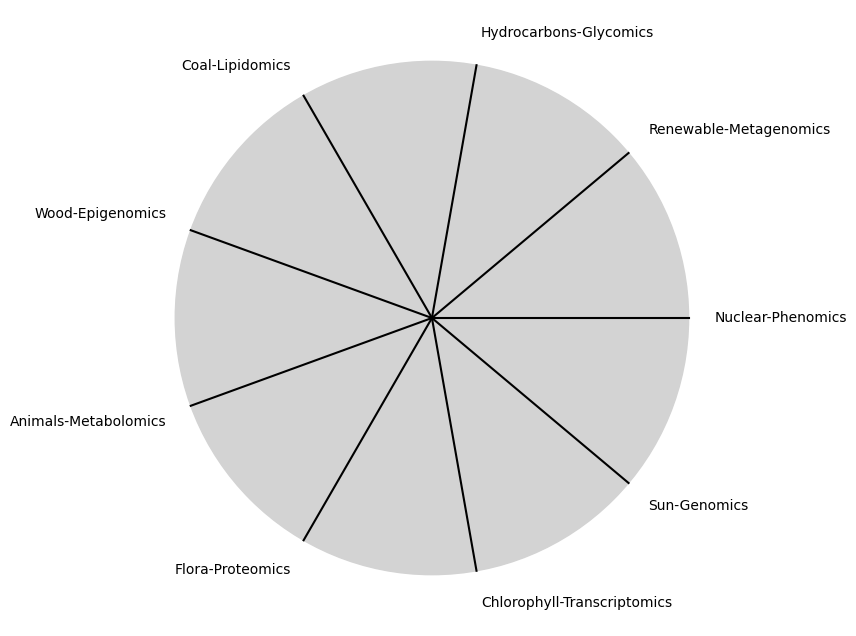
\(\%\) Overcoming, Self#
\(\alpha, \beta, t\) NexToken:
Parametrizedthe processes that are responsible for human behavior as a moiety of “chains” with some “wiggle-room”
Show code cell source
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Clock settings; f(t) random disturbances making "paradise lost"
clock_face_radius = 1.0
number_of_ticks = 9
tick_labels = [
"Sun-Genomics", "Chlorophyll-Transcriptomics", "Flora-Proteomics", "Animals-Metabolomics",
"Wood-Epigenomics", "Coal-Lipidomics", "Hydrocarbons-Glycomics", "Renewable-Metagenomics", "Nuclear-Phenomics"
]
# Calculate the angles for each tick (in radians)
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, number_of_ticks, endpoint=False)
# Inverting the order to make it counterclockwise
angles = angles[::-1]
# Create figure and axis
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
ax.set_xlim(-1.2, 1.2)
ax.set_ylim(-1.2, 1.2)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# Draw the clock face
clock_face = plt.Circle((0, 0), clock_face_radius, color='lightgrey', fill=True)
ax.add_patch(clock_face)
# Draw the ticks and labels
for angle, label in zip(angles, tick_labels):
x = clock_face_radius * np.cos(angle)
y = clock_face_radius * np.sin(angle)
# Draw the tick
ax.plot([0, x], [0, y], color='black')
# Positioning the labels slightly outside the clock face
label_x = 1.1 * clock_face_radius * np.cos(angle)
label_y = 1.1 * clock_face_radius * np.sin(angle)
# Adjusting label alignment based on its position
ha = 'center'
va = 'center'
if np.cos(angle) > 0:
ha = 'left'
elif np.cos(angle) < 0:
ha = 'right'
if np.sin(angle) > 0:
va = 'bottom'
elif np.sin(angle) < 0:
va = 'top'
ax.text(label_x, label_y, label, horizontalalignment=ha, verticalalignment=va, fontsize=10)
# Remove axes
ax.axis('off')
# Show the plot
plt.show()
Show code cell output
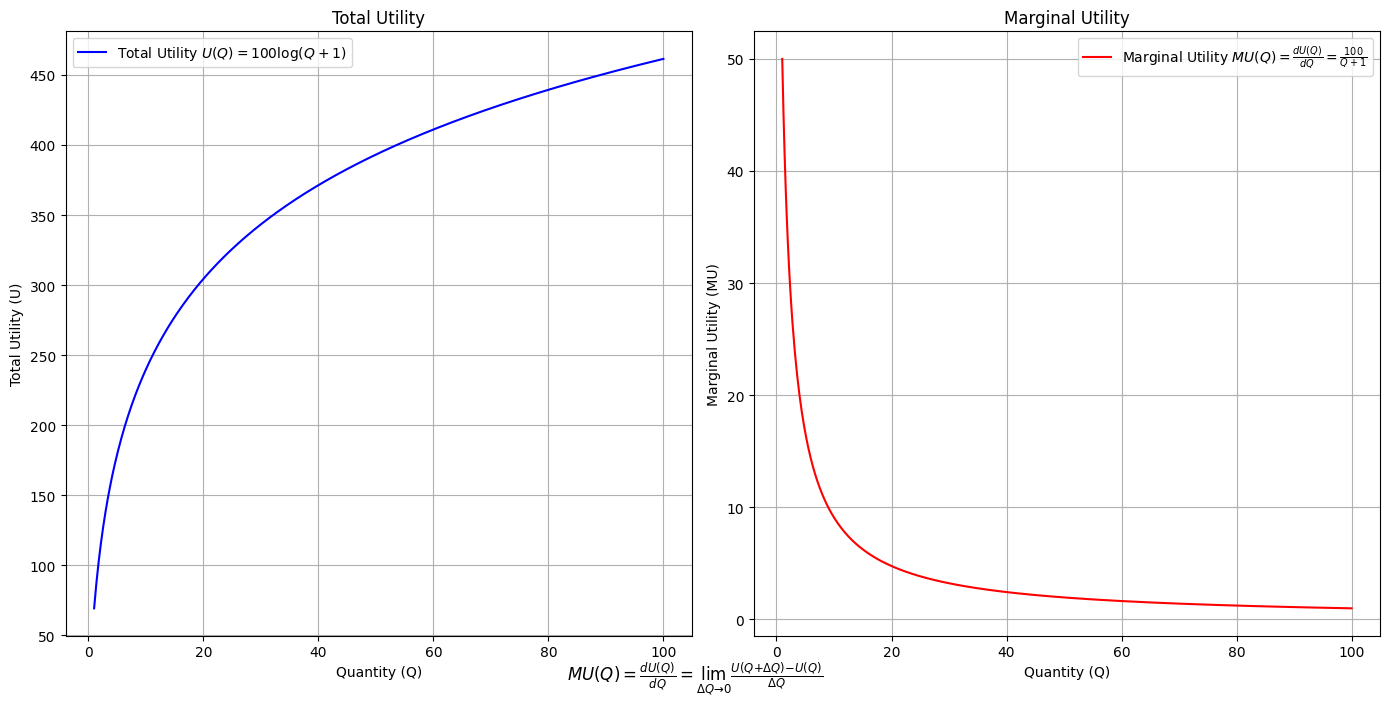
\(SV_t'\) Emotion:
Ultimategoal of life, where all the outlined elements converge. It’s the subjective experience or illusion that life should evoke, the connection between god, neighbor, and self.Thusminor chords may represent “loose” chains whereas dom7 & half-dim are somewhat “tight” chains constraining us to our sense of thenextoken
Show code cell source
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define the total utility function U(Q)
def total_utility(Q):
return 100 * np.log(Q + 1) # Logarithmic utility function for illustration
# Define the marginal utility function MU(Q)
def marginal_utility(Q):
return 100 / (Q + 1) # Derivative of the total utility function
# Generate data
Q = np.linspace(1, 100, 500) # Quantity range from 1 to 100
U = total_utility(Q)
MU = marginal_utility(Q)
# Plotting
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 7))
# Plot Total Utility
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(Q, U, label=r'Total Utility $U(Q) = 100 \log(Q + 1)$', color='blue')
plt.title('Total Utility')
plt.xlabel('Quantity (Q)')
plt.ylabel('Total Utility (U)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
# Plot Marginal Utility
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(Q, MU, label=r'Marginal Utility $MU(Q) = \frac{dU(Q)}{dQ} = \frac{100}{Q + 1}$', color='red')
plt.title('Marginal Utility')
plt.xlabel('Quantity (Q)')
plt.ylabel('Marginal Utility (MU)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
# Adding some calculus notation and Greek symbols
plt.figtext(0.5, 0.02, r"$MU(Q) = \frac{dU(Q)}{dQ} = \lim_{\Delta Q \to 0} \frac{U(Q + \Delta Q) - U(Q)}{\Delta Q}$", ha="center", fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Show code cell output
Show code cell source
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.cm import ScalarMappable
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap, PowerNorm
def gaussian(x, mean, std_dev, amplitude=1):
return amplitude * np.exp(-0.9 * ((x - mean) / std_dev) ** 2)
def overlay_gaussian_on_line(ax, start, end, std_dev):
x_line = np.linspace(start[0], end[0], 100)
y_line = np.linspace(start[1], end[1], 100)
mean = np.mean(x_line)
y = gaussian(x_line, mean, std_dev, amplitude=std_dev)
ax.plot(x_line + y / np.sqrt(2), y_line + y / np.sqrt(2), color='red', linewidth=2.5)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
intervals = np.linspace(0, 100, 11)
custom_means = np.linspace(1, 23, 10)
custom_stds = np.linspace(.5, 10, 10)
# Change to 'viridis' colormap to get gradations like the older plot
cmap = plt.get_cmap('viridis')
norm = plt.Normalize(custom_stds.min(), custom_stds.max())
sm = ScalarMappable(cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
sm.set_array([])
median_points = []
for i in range(10):
xi, xf = intervals[i], intervals[i+1]
x_center, y_center = (xi + xf) / 2 - 20, 100 - (xi + xf) / 2 - 20
x_curve = np.linspace(custom_means[i] - 3 * custom_stds[i], custom_means[i] + 3 * custom_stds[i], 200)
y_curve = gaussian(x_curve, custom_means[i], custom_stds[i], amplitude=15)
x_gauss = x_center + x_curve / np.sqrt(2)
y_gauss = y_center + y_curve / np.sqrt(2) + x_curve / np.sqrt(2)
ax.plot(x_gauss, y_gauss, color=cmap(norm(custom_stds[i])), linewidth=2.5)
median_points.append((x_center + custom_means[i] / np.sqrt(2), y_center + custom_means[i] / np.sqrt(2)))
median_points = np.array(median_points)
ax.plot(median_points[:, 0], median_points[:, 1], '--', color='grey')
start_point = median_points[0, :]
end_point = median_points[-1, :]
overlay_gaussian_on_line(ax, start_point, end_point, 24)
ax.grid(True, linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5, color='grey')
ax.set_xlim(-30, 111)
ax.set_ylim(-20, 87)
# Create a new ScalarMappable with a reversed colormap just for the colorbar
cmap_reversed = plt.get_cmap('viridis').reversed()
sm_reversed = ScalarMappable(cmap=cmap_reversed, norm=norm)
sm_reversed.set_array([])
# Existing code for creating the colorbar
cbar = fig.colorbar(sm_reversed, ax=ax, shrink=1, aspect=90)
# Specify the tick positions you want to set
custom_tick_positions = [0.5, 5, 8, 10] # example positions, you can change these
cbar.set_ticks(custom_tick_positions)
# Specify custom labels for those tick positions
custom_tick_labels = ['5', '3', '1', '0'] # example labels, you can change these
cbar.set_ticklabels(custom_tick_labels)
# Label for the colorbar
cbar.set_label(r'♭', rotation=0, labelpad=15, fontstyle='italic', fontsize=24)
# Label for the colorbar
cbar.set_label(r'♭', rotation=0, labelpad=15, fontstyle='italic', fontsize=24)
cbar.set_label(r'♭', rotation=0, labelpad=15, fontstyle='italic', fontsize=24)
# Add X and Y axis labels with custom font styles
ax.set_xlabel(r'Principal Component', fontstyle='italic')
ax.set_ylabel(r'Emotional State', rotation=0, fontstyle='italic', labelpad=15)
# Add musical modes as X-axis tick labels
# musical_modes = ["Ionian", "Dorian", "Phrygian", "Lydian", "Mixolydian", "Aeolian", "Locrian"]
greek_letters = ['α', 'β','γ', 'δ', 'ε', 'ζ', 'η'] # 'θ' , 'ι', 'κ'
mode_positions = np.linspace(ax.get_xlim()[0], ax.get_xlim()[1], len(greek_letters))
ax.set_xticks(mode_positions)
ax.set_xticklabels(greek_letters, rotation=0)
# Add moods as Y-axis tick labels
moods = ["flow", "control", "relaxed", "bored", "apathy","worry", "anxiety", "arousal"]
mood_positions = np.linspace(ax.get_ylim()[0], ax.get_ylim()[1], len(moods))
ax.set_yticks(mood_positions)
ax.set_yticklabels(moods)
# ... (rest of the code unchanged)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Show code cell output
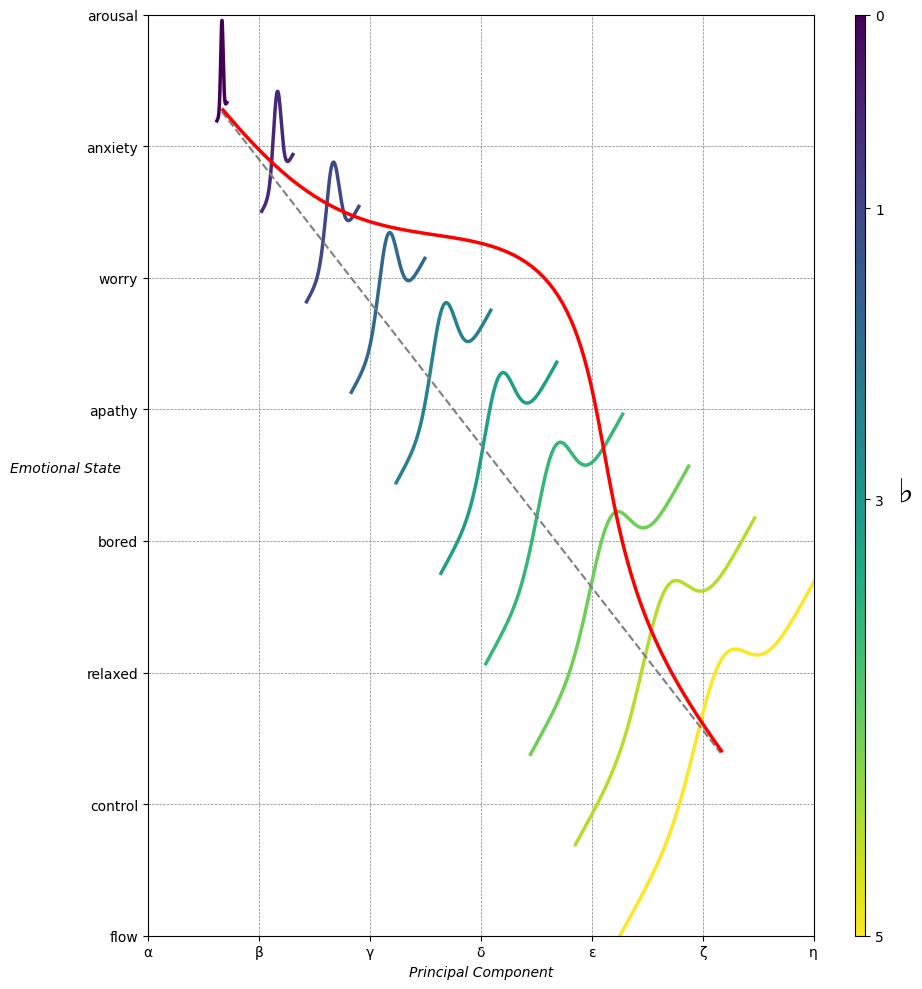

Emotion & Affect as Outcomes & Freewill. And the predictors \(\beta\) are MQ-TEA: Modes (ionian, dorian, phrygian, lydian, mixolydian, locrian), Qualities (major, minor, dominant, suspended, diminished, half-dimished, augmented), Tensions (7th), Extensions (9th, 11th, 13th), and Alterations (♯, ♭) 33#
1. Exposure
\
2. Role -> 4. Categorical.Imperative -> 5. Determinism -> 6. Freewill
/
3. Impulse