Music#
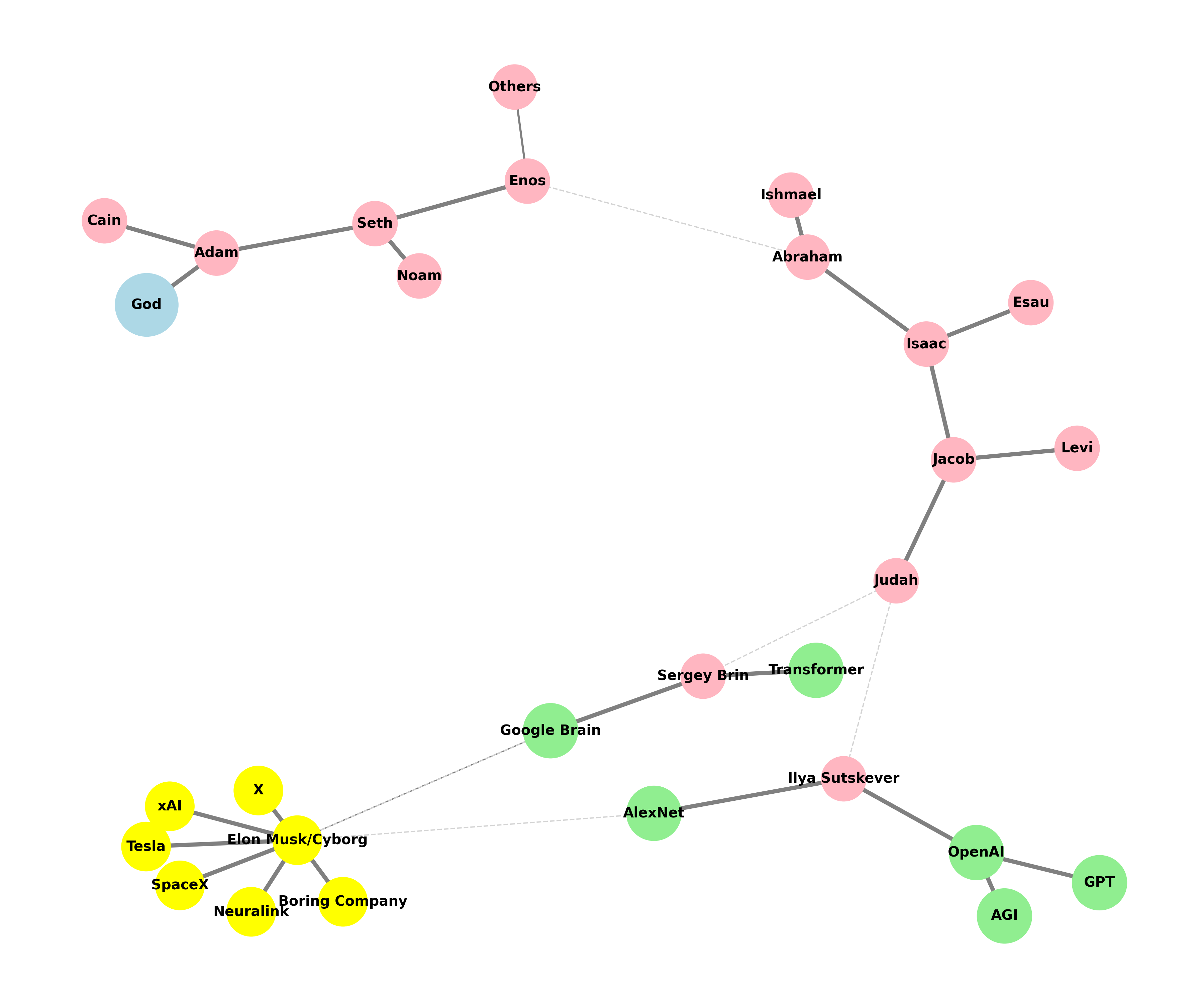
Departure, struggle, return#
From the point of view of form, the archetype of all the arts is the musicians
1. Phonetics
\
2. Temperament -> 4. Modes -> 5. NexToken -> 6. Emotion
/
3. Scales

These six topics cover all aspects of music. Challenge GPT-4o or any other ChatBot to find a issue that isn’t seamlessly subsumed by one of these headlines#

Pretty Boy Swag by Soulja Boy Tell ‘Em. An eloquent example of a half-Phrygian scale (III-♭II-i) that is quite extensively used in Trap Musik#

Reharming a very well known nursery & kindergarten melody. Don’t focus on the “pocket” and groove, or lack thereof. Just stick to the idea for now#
Show code cell source
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Create a directed graph
G = nx.DiGraph()
# Add nodes representing different levels (subatomic, atomic, cosmic, financial, social)
levels = ['i: Return', 'ii7♭5: Departure', 'V7: Struggle']
# Add nodes to the graph
G.add_nodes_from(levels)
# Add edges to represent the flow of information (photons)
# Assuming the flow is directional from more fundamental levels to more complex ones
edges = [('ii7♭5: Departure', 'V7: Struggle'),
('V7: Struggle', 'i: Return'),]
# Add edges to the graph
G.add_edges_from(edges)
# Define positions for the nodes in a circular layout
pos = nx.circular_layout(G)
# Set the figure size (width, height)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10)) # Adjust the size as needed
# Draw the main nodes
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G, pos, node_color='lightblue', node_size=30000)
# Draw the edges with arrows and create space between the arrowhead and the node
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, pos, arrowstyle='->', arrowsize=20, edge_color='grey',
connectionstyle='arc3,rad=0.2') # Adjust rad for more/less space
# Add smaller red nodes (photon nodes) exactly on the circular layout
for edge in edges:
# Calculate the vector between the two nodes
vector = pos[edge[1]] - pos[edge[0]]
# Calculate the midpoint
mid_point = pos[edge[0]] + 0.5 * vector
# Normalize to ensure it's on the circle
radius = np.linalg.norm(pos[edge[0]])
mid_point_on_circle = mid_point / np.linalg.norm(mid_point) * radius
# Draw the small red photon node at the midpoint on the circular layout
plt.scatter(mid_point_on_circle[0], mid_point_on_circle[1], c='lightpink', s=500, zorder=3)
# Draw a small lime green arrow inside the red node to indicate direction
arrow_vector = vector / np.linalg.norm(vector) * 0.1 # Scale down arrow size
plt.arrow(mid_point_on_circle[0] - 0.05 * arrow_vector[0],
mid_point_on_circle[1] - 0.05 * arrow_vector[1],
arrow_vector[0], arrow_vector[1],
head_width=0.03, head_length=0.05, fc='limegreen', ec='limegreen', zorder=4)
# Draw the labels for the main nodes
nx.draw_networkx_labels(G, pos, font_size=18, font_weight='normal')
# Add a legend for "Photon/Info"
plt.scatter([], [], c='lightpink', s=100, label='Chord Progression') # Empty scatter for the legend
plt.legend(scatterpoints=1, frameon=True, labelspacing=1, loc='upper right')
# Set the title and display the plot
plt.title('Emotional Arc', fontsize=15)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
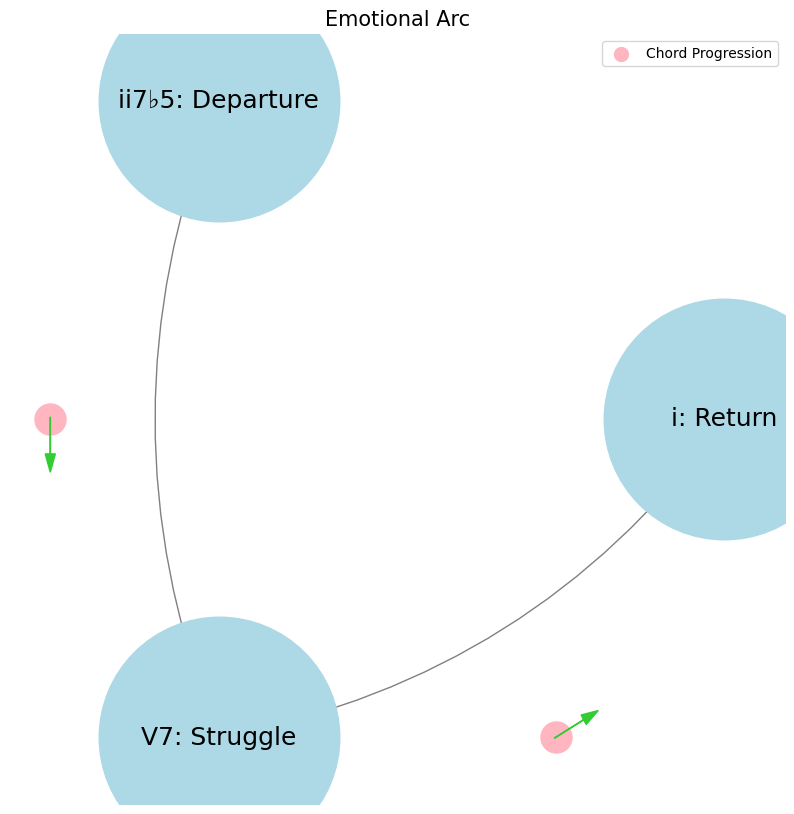

Predicting the Next Token. Three minor (ii, iii, vi), two major (I & IV), a dom7 & a half-dim7 constitute the diatonic chords of western music in order of degree of tension they invoke in the conditioned listener. For these reasons, dom7 & half-dim7 are the strongest predictors of the next chord in any chord sequence (progression or non-progression). Because the composer, performer, and listener crave some relief. Minor chords are associated with the most ambiguity because there are three of them and thus more options when compared to the other diatonic groups. Major chords are intermediate in ambiguity. We can speak with a degree of accuracy that a half-dim7 resolves to the V7 especially in the aeolian mode. The dom7 will resolve to the root but or to a secondary dominant. Not to mention that there are two species of dom7: the one that resolves to a major (has extensions: dom13) and the one that resolves to a minor (has alterations: dom7♭9♯9♭13). So one might actually claim that dom7 is really two different chords and, thus, as ambiguous as the two majors. But the two majors do not strongly predict a next token since they aren’t very tense. They might be followed by yet another non-tense chords or by a tense chord.#
ii \(\mu\) Single Note#
ii\(f(t)\) Phonetics: 41 42Fractals\(440Hz \times 2^{\frac{N}{12}}\), \(S_0(t) \times e^{logHR}\), \(\frac{S N(d_1)}{K N(d_2)} \times e^{rT}\)
Show code cell source
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Parameters
sample_rate = 44100 # Hz
duration = 20.0 # seconds
A4_freq = 440.0 # Hz
# Time array
t = np.linspace(0, duration, int(sample_rate * duration), endpoint=False)
# Fundamental frequency (A4)
signal = np.sin(2 * np.pi * A4_freq * t)
# Adding overtones (harmonics)
harmonics = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] # First few harmonics
amplitudes = [0.5, 0.25, 0.15, 0.1, 0.05, 0.03, 0.01, 0.005] # Amplitudes for each harmonic
for i, harmonic in enumerate(harmonics):
signal += amplitudes[i] * np.sin(2 * np.pi * A4_freq * harmonic * t)
# Perform FFT (Fast Fourier Transform)
N = len(signal)
yf = np.fft.fft(signal)
xf = np.fft.fftfreq(N, 1 / sample_rate)
# Plot the frequency spectrum
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(xf[:N//2], 2.0/N * np.abs(yf[:N//2]), color='navy', lw=1.5)
# Aesthetics improvements
plt.title('Simulated Frequency Spectrum of A440 on a Grand Piano', fontsize=16, weight='bold')
plt.xlabel('Frequency (Hz)', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=14)
plt.xlim(0, 4186) # Limit to the highest frequency on a piano (C8)
plt.ylim(0, None)
# Shading the region for normal speaking range (approximately 85 Hz to 255 Hz)
plt.axvspan(500, 2000, color='lightpink', alpha=0.5)
# Annotate the shaded region
plt.annotate('Normal Speaking Range (500 Hz - 2000 Hz)',
xy=(2000, 0.7), xycoords='data',
xytext=(2500, 0.5), textcoords='data',
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', arrowstyle="->"),
fontsize=12, color='black')
# Remove top and right spines
plt.gca().spines['top'].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines['right'].set_visible(False)
# Customize ticks
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
# Light grid
plt.grid(color='grey', linestyle=':', linewidth=0.5)
# Show the plot
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Show code cell output
V7\(S(t)\) Temperament: \(440Hz \times 2^{\frac{N}{12}}\)i\(h(t)\) Scales: 12 unique notes x 7 modes (Bach covers only x 2 modes in WTK)Soulja Boy has an incomplete Phrygian in PBS
Flamenco Phyrgian scale is equivalent to a Mixolydian
V9♭♯9♭13
V7 \(\sigma\) Chord Stacks#
\((X'X)^T \cdot X'Y\): Mode: \( \mathcal{F}(t) = \alpha \cdot \left( \prod_{i=1}^{n} \frac{\partial \psi_i(t)}{\partial t} \right) + \beta \cdot \int_{0}^{t} \left( \sum_{j=1}^{m} \frac{\partial \phi_j(\tau)}{\partial \tau} \right) d\tau\)
Show code cell source
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Clock settings; f(t) random disturbances making "paradise lost"
clock_face_radius = 1.0
number_of_ticks = 7
tick_labels = [
"Root-iADL (i)",
"Hunter-gather (ii7♭5)", "Peasant (III)", "Farmer (iv)", "Manufacturer (V7♭9♯9♭13)",
"Energy (VI)", "Transport (VII)"
]
# Calculate the angles for each tick (in radians)
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, number_of_ticks, endpoint=False)
# Inverting the order to make it counterclockwise
angles = angles[::-1]
# Create figure and axis
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
ax.set_xlim(-1.2, 1.2)
ax.set_ylim(-1.2, 1.2)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# Draw the clock face
clock_face = plt.Circle((0, 0), clock_face_radius, color='lightgrey', fill=True)
ax.add_patch(clock_face)
# Draw the ticks and labels
for angle, label in zip(angles, tick_labels):
x = clock_face_radius * np.cos(angle)
y = clock_face_radius * np.sin(angle)
# Draw the tick
ax.plot([0, x], [0, y], color='black')
# Positioning the labels slightly outside the clock face
label_x = 1.1 * clock_face_radius * np.cos(angle)
label_y = 1.1 * clock_face_radius * np.sin(angle)
# Adjusting label alignment based on its position
ha = 'center'
va = 'center'
if np.cos(angle) > 0:
ha = 'left'
elif np.cos(angle) < 0:
ha = 'right'
if np.sin(angle) > 0:
va = 'bottom'
elif np.sin(angle) < 0:
va = 'top'
ax.text(label_x, label_y, label, horizontalalignment=ha, verticalalignment=va, fontsize=10)
# Remove axes
ax.axis('off')
# Show the plot
plt.show()
Show code cell output
i \(\%\) Predict NexToken#
\(\alpha, \beta, t\) NexToken: Attention, to the minor, major, dom7, and half-dim7 groupings, is all you need 43
Show code cell source
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Clock settings; f(t) random disturbances making "paradise lost"
clock_face_radius = 1.0
number_of_ticks = 9
tick_labels = [
"Sun-Genomics", "Chlorophyll-Transcriptomics", "Flora-Proteomics", "Animals-Metabolomics",
"Wood-Epigenomics", "Coal-Lipidomics", "Hydrocarbons-Glycomics", "Renewable-Metagenomics", "Nuclear-Phenomics"
]
# Calculate the angles for each tick (in radians)
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, number_of_ticks, endpoint=False)
# Inverting the order to make it counterclockwise
angles = angles[::-1]
# Create figure and axis
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
ax.set_xlim(-1.2, 1.2)
ax.set_ylim(-1.2, 1.2)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# Draw the clock face
clock_face = plt.Circle((0, 0), clock_face_radius, color='lightgrey', fill=True)
ax.add_patch(clock_face)
# Draw the ticks and labels
for angle, label in zip(angles, tick_labels):
x = clock_face_radius * np.cos(angle)
y = clock_face_radius * np.sin(angle)
# Draw the tick
ax.plot([0, x], [0, y], color='black')
# Positioning the labels slightly outside the clock face
label_x = 1.1 * clock_face_radius * np.cos(angle)
label_y = 1.1 * clock_face_radius * np.sin(angle)
# Adjusting label alignment based on its position
ha = 'center'
va = 'center'
if np.cos(angle) > 0:
ha = 'left'
elif np.cos(angle) < 0:
ha = 'right'
if np.sin(angle) > 0:
va = 'bottom'
elif np.sin(angle) < 0:
va = 'top'
ax.text(label_x, label_y, label, horizontalalignment=ha, verticalalignment=va, fontsize=10)
# Remove axes
ax.axis('off')
# Show the plot
plt.show()
Show code cell output
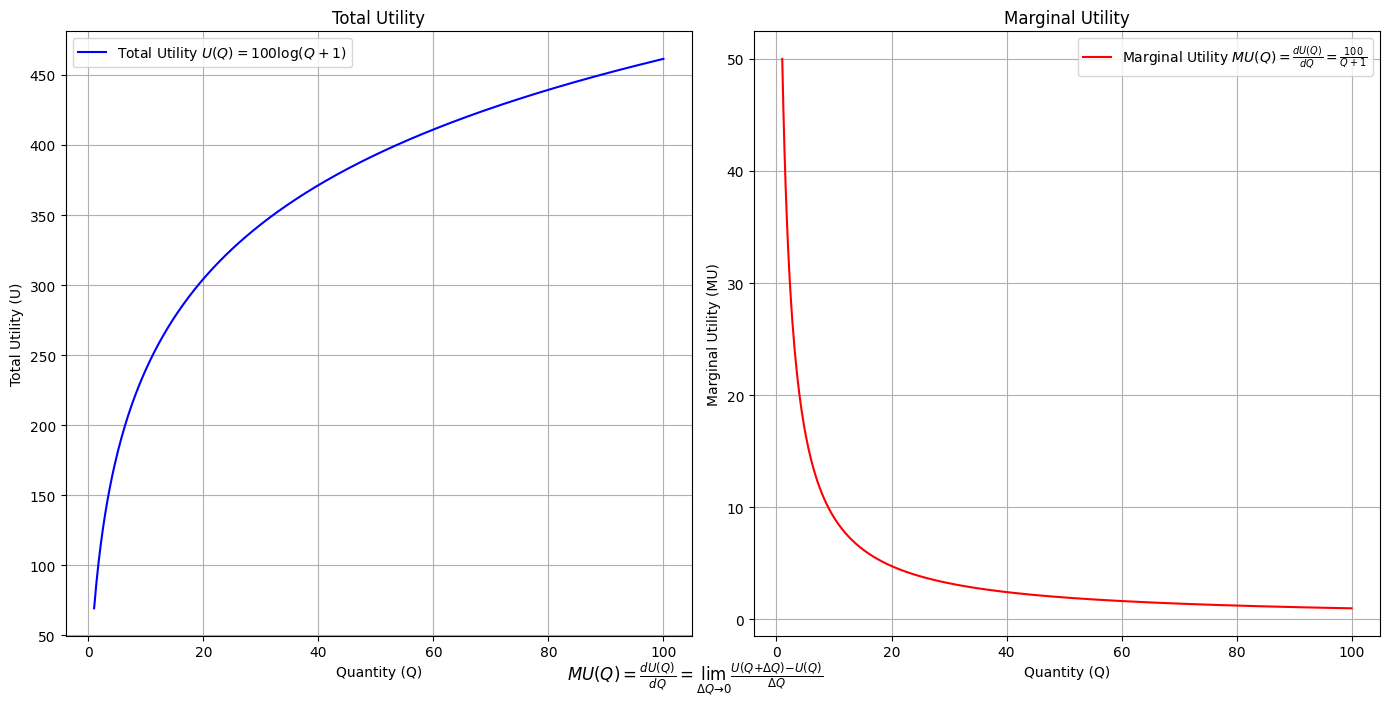
\(SV_t'\) Emotion: How many degrees of freedom does a composer, performer, or audience member have within a genre? We’ve roped in the audience as a reminder that music has no passive participants
Show code cell source
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define the total utility function U(Q)
def total_utility(Q):
return 100 * np.log(Q + 1) # Logarithmic utility function for illustration
# Define the marginal utility function MU(Q)
def marginal_utility(Q):
return 100 / (Q + 1) # Derivative of the total utility function
# Generate data
Q = np.linspace(1, 100, 500) # Quantity range from 1 to 100
U = total_utility(Q)
MU = marginal_utility(Q)
# Plotting
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 7))
# Plot Total Utility
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(Q, U, label=r'Total Utility $U(Q) = 100 \log(Q + 1)$', color='blue')
plt.title('Total Utility')
plt.xlabel('Quantity (Q)')
plt.ylabel('Total Utility (U)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
# Plot Marginal Utility
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(Q, MU, label=r'Marginal Utility $MU(Q) = \frac{dU(Q)}{dQ} = \frac{100}{Q + 1}$', color='red')
plt.title('Marginal Utility')
plt.xlabel('Quantity (Q)')
plt.ylabel('Marginal Utility (MU)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
# Adding some calculus notation and Greek symbols
plt.figtext(0.5, 0.02, r"$MU(Q) = \frac{dU(Q)}{dQ} = \lim_{\Delta Q \to 0} \frac{U(Q + \Delta Q) - U(Q)}{\Delta Q}$", ha="center", fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Show code cell output
Show code cell source
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.cm import ScalarMappable
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap, PowerNorm
def gaussian(x, mean, std_dev, amplitude=1):
return amplitude * np.exp(-0.9 * ((x - mean) / std_dev) ** 2)
def overlay_gaussian_on_line(ax, start, end, std_dev):
x_line = np.linspace(start[0], end[0], 100)
y_line = np.linspace(start[1], end[1], 100)
mean = np.mean(x_line)
y = gaussian(x_line, mean, std_dev, amplitude=std_dev)
ax.plot(x_line + y / np.sqrt(2), y_line + y / np.sqrt(2), color='red', linewidth=2.5)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
intervals = np.linspace(0, 100, 11)
custom_means = np.linspace(1, 23, 10)
custom_stds = np.linspace(.5, 10, 10)
# Change to 'viridis' colormap to get gradations like the older plot
cmap = plt.get_cmap('viridis')
norm = plt.Normalize(custom_stds.min(), custom_stds.max())
sm = ScalarMappable(cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
sm.set_array([])
median_points = []
for i in range(10):
xi, xf = intervals[i], intervals[i+1]
x_center, y_center = (xi + xf) / 2 - 20, 100 - (xi + xf) / 2 - 20
x_curve = np.linspace(custom_means[i] - 3 * custom_stds[i], custom_means[i] + 3 * custom_stds[i], 200)
y_curve = gaussian(x_curve, custom_means[i], custom_stds[i], amplitude=15)
x_gauss = x_center + x_curve / np.sqrt(2)
y_gauss = y_center + y_curve / np.sqrt(2) + x_curve / np.sqrt(2)
ax.plot(x_gauss, y_gauss, color=cmap(norm(custom_stds[i])), linewidth=2.5)
median_points.append((x_center + custom_means[i] / np.sqrt(2), y_center + custom_means[i] / np.sqrt(2)))
median_points = np.array(median_points)
ax.plot(median_points[:, 0], median_points[:, 1], '--', color='grey')
start_point = median_points[0, :]
end_point = median_points[-1, :]
overlay_gaussian_on_line(ax, start_point, end_point, 24)
ax.grid(True, linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5, color='grey')
ax.set_xlim(-30, 111)
ax.set_ylim(-20, 87)
# Create a new ScalarMappable with a reversed colormap just for the colorbar
cmap_reversed = plt.get_cmap('viridis').reversed()
sm_reversed = ScalarMappable(cmap=cmap_reversed, norm=norm)
sm_reversed.set_array([])
# Existing code for creating the colorbar
cbar = fig.colorbar(sm_reversed, ax=ax, shrink=1, aspect=90)
# Specify the tick positions you want to set
custom_tick_positions = [0.5, 5, 8, 10] # example positions, you can change these
cbar.set_ticks(custom_tick_positions)
# Specify custom labels for those tick positions
custom_tick_labels = ['5', '3', '1', '0'] # example labels, you can change these
cbar.set_ticklabels(custom_tick_labels)
# Label for the colorbar
cbar.set_label(r'♭', rotation=0, labelpad=15, fontstyle='italic', fontsize=24)
# Label for the colorbar
cbar.set_label(r'♭', rotation=0, labelpad=15, fontstyle='italic', fontsize=24)
cbar.set_label(r'♭', rotation=0, labelpad=15, fontstyle='italic', fontsize=24)
# Add X and Y axis labels with custom font styles
ax.set_xlabel(r'Principal Component', fontstyle='italic')
ax.set_ylabel(r'Emotional State', rotation=0, fontstyle='italic', labelpad=15)
# Add musical modes as X-axis tick labels
# musical_modes = ["Ionian", "Dorian", "Phrygian", "Lydian", "Mixolydian", "Aeolian", "Locrian"]
greek_letters = ['α', 'β','γ', 'δ', 'ε', 'ζ', 'η'] # 'θ' , 'ι', 'κ'
mode_positions = np.linspace(ax.get_xlim()[0], ax.get_xlim()[1], len(greek_letters))
ax.set_xticks(mode_positions)
ax.set_xticklabels(greek_letters, rotation=0)
# Add moods as Y-axis tick labels
moods = ["flow", "control", "relaxed", "bored", "apathy","worry", "anxiety", "arousal"]
mood_positions = np.linspace(ax.get_ylim()[0], ax.get_ylim()[1], len(moods))
ax.set_yticks(mood_positions)
ax.set_yticklabels(moods)
# ... (rest of the code unchanged)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Show code cell output
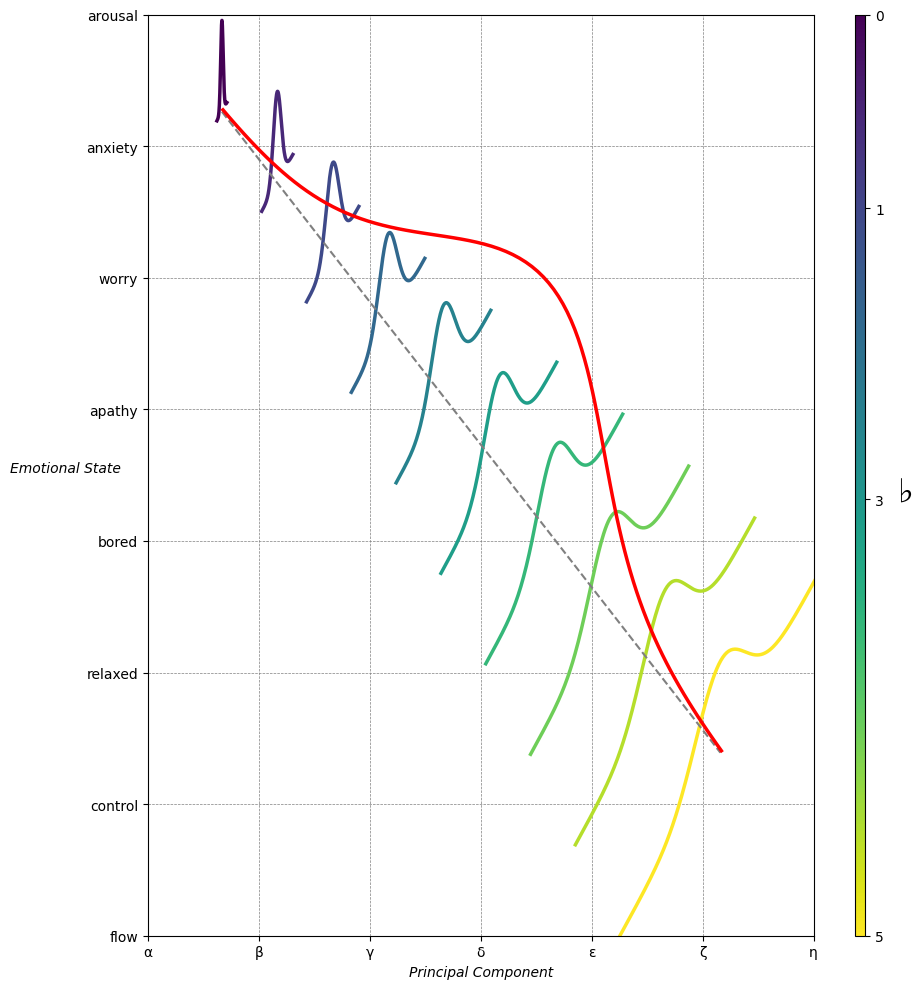

Emotion & Affect as Outcomes & Freewill. And the predictors \(\beta\) are MQ-TEA: Modes (ionian, dorian, phrygian, lydian, mixolydian, locrian), Qualities (major, minor, dominant, suspended, diminished, half-dimished, augmented), Tensions (7th), Extensions (9th, 11th, 13th), and Alterations (♯, ♭) 44#
1. f(t)
\
2. S(t) -> 4. Nxb:t(X'X).X'Y -> 5. b -> 6. df
/
3. h(t)